What is a PID Controller?
Just to get it out of the way, PID stands for “Proportional, Integral, Derivative,” and has to do with how the controller does what it does. Rather than go into that level of detail, this page is going to focus instead on the results of using PID control. If you’re interested in reading more about the inner workings of PID, the wikipedia article is quite detailed. Let’s get started.
An easy to explain what PID control is, is to first look at what it isn’t. If you were to graph the temperature in your home oven, it would look something like this.
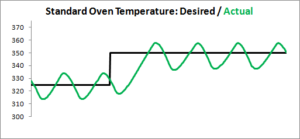
You can see that we’re asking for 325, then 350 degrees. The actual temperature cycles above and below these values. Depending on the oven, the oscillations can be quite large. +/- 25 degrees is not uncommon.
Now let’s take a look at the same oven, controlled using PID:
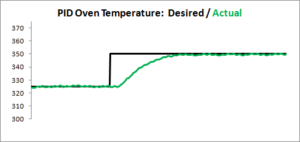
So, quite a bit better. Why does this happen? The key is to look at how the oven is being driven. A standard oven uses something called “On-Off” control.
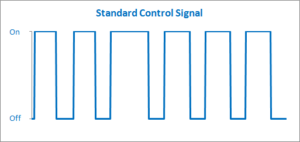
Essentially, it’s saying: “If I’m above my desired value, turn off. If I’m below desired, turn on.” This is a really reliable way of doing things, but as we saw above, it generally isn’t very precise.
PID control is a little more complex. Instead of just “On” or “Off”, a PID controller outputs a value somewhere between 0 and 100%.
Here’s how the PID controller drove the oven in the graph above.
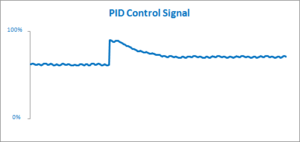
Rather than jerking the oven around with full on and full off signals, the PID controller was able to sit at an intermediate value.
This is how it achieved more precise, gentle control.
Of course there’s more to it than this, but hopefully this will help you decide if this is something you want to examine further.
Information provided by http://www.ospid.com/blog/what-is-pid-control/
